Research Approaches
Molecular biology (shotgun cloning, PCR, qPCR, RT-qPCR, sanger sequencing)
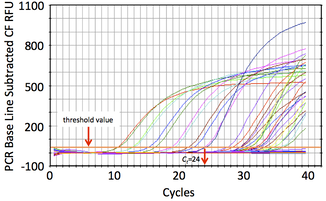
The structural and functional diversity of microbial communities can be studied using culture-independent methods that target DNA, RNA, and proteins.
Systems biology ('omics' approaches)
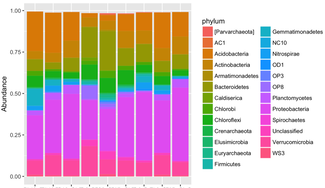
High-throughput 'omics' approaches allow a more comprehensive understanding of microbial responses to a changing environment.
Spectroscopy (CLSM, SEM, TEM)
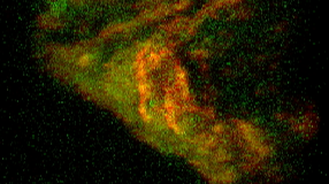
"Seeing is believing." Microbial communities can be observed using a variety of microscopes, from confocal laser scanning microscope to electron microscopes.
Analytical chemistry (GC-MS/MS, LC-MS/MS, isotopic analysis, Raman)
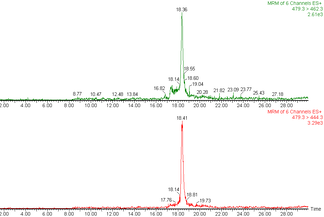
Microbial contribution to biogeochemical cycles on the Earth can be probed using analytic chemical techniques, from isotopic/radioactive analysis and AAS to GC/LC-MS/MS and to FTIR, Raman, XPS, STXM and nanoSIMS.
Mathematical modeling and numerical simulation
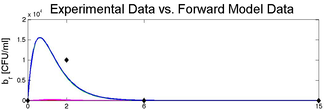
Dynamics of many microbial activities can be depicted using mathematical models and numerical simulation, allowing more quantitative mechanistic understanding of coupled processes.